Search Results for: hypothesis
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
Hypothesis
What Is Hypothesis? A scientific hypothesis is a foundational element of the scientific method. It's a testable statement... Read More
Alternative hypothesis
Definition noun The hypothesis accepted to be true if the null hypothesis is rejected based on statistical... Read More
RNA-DNA World Hypothesis?
How did life start as we know it? In the scientific community, the "RNA World Hypothesis" has many adherents. Many believed... Read More
Redundancy Hypothesis
Definition noun A theory that assumes one or more species impart a role within an ecological unit to maintain dynamic... Read More
Michaelis-menten hypothesis
Michaelis-Menten hypothesis (Science: chemistry) That a complex is formed between an enzyme and its substrate (the... Read More
Rivet Hypothesis
Definition noun It is a theory that entails about the conditions of ecosystem wherein a significant loss of a certain... Read More
Recent single-origin hypothesis
Definition noun The hypothesis that modern humans came from or evolved from a single origin (i.e. in Africa) and then these... Read More
Chemiosmotic coupling hypothesis
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Gene Action – Operon Hypothesis
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Some genes are switched on or off depending on environmental conditions. The... Read More
Chemiosmotic hypothesis
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Wobble hypothesis
wobble hypothesis (Science: molecular biology) explains why the base inosine is included in position 1 in the anticodons of... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
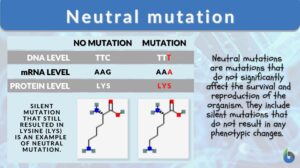
Neutral mutation
Neutral Mutation Definition What is a neutral mutation? Neutral mutations are the alterations in the DNA that are... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
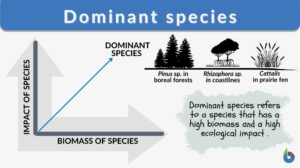
Dominant species
Dominance is the state of being supreme or dominant. Community dominance refers to the form of dominance where certain... Read More
Abiogenesis
Definition noun plural: abiogeneses a·bi·o·gen·e·sis, eɪbaɪəʊˈdʒɛnəsɪs (1) The idea that primitive life... Read More
Wilcoxon rank-sum test
Definition noun A non-parametric test of two samples which support exclusively on the order of observations in which the two... Read More
Erwin Chargaff
Quick Info (person) A biochemist known for his proposed Chargaff's rules that led to the discovery of the double helical... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
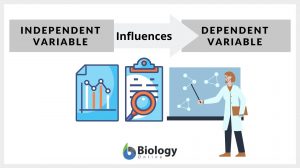
Independent variable
Independent Variable Definition To define an independent variable, let us first understand what a variable is. The word... Read More
Susceptible
Resistance, vulnerability, sensitivity, tolerance, and susceptibility are some highly important terminologies across the... Read More
Spontaneous generation
Definition noun plural: spontaneous generations The previously popular notion that living organisms arise or develop from... Read More
Particulate inheritance
Definition noun (genetics) A theory formulated by Gregor Mendel based on his garden pea breeding experiments wherein he... Read More
Replacement model
Definition noun A theory proposed by Christopher Stringer and Peter Andrews suggesting that the place of origin of modern... Read More
On Mate Selection Evolution: Are intelligent males more attractive?
A study published in Science on January 11 seems to be the first to lay empirical evidence that concur with Charles Darwin's... Read More
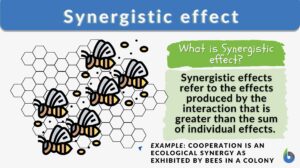
Synergistic effect
Synergistic Effects Definition In biology, synergistic effects are the effects when chemical substances or biological... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Steroid hormone
Definition noun, plural: steroid hormones A type of steroid that acts as a hormone, and that which is exemplified by sex... Read More
Chemiosmotic theory
Definition noun A theory postulated by the biochemist Peter Mitchell in 1961 to describe ATP synthesis by way of a proton... Read More
Last universal ancestor
Definition noun The hypothetical primordial organism from which all other species of organisms on Earth... Read More
Scientific method
Definition noun A systematic approach to solving a problem by discovering knowledge, investigating a phenomenon, verifying... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More