Search Results for: induction
Gibberellins and Gibberellic Acid
The family of gibberellins have a similar effect to that of auxins; they promote cell division and elongation. The major... Read More
Gene Action – Operon Hypothesis
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Some genes are switched on or off depending on environmental conditions. The... Read More
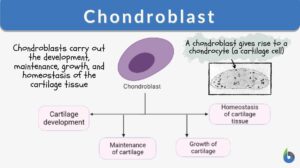
Chondroblast
There are two forms of cells in cartilage: chondroblasts and chondrocytes. The chondroblasts are cells that secrete the... Read More
Glycocalyx
What is the Glycocalyx? The glycocalyx is a polysaccharide-based gel-like, highly hydrous cellular thin layer, covering... Read More
Diaphoresis
What is Diaphoresis? Diaphoresis is referred to excessive or profuse perspiration or sweating which may be due to... Read More
Inductothermy
Inductothermy artificial fever production by means of electromagnetic induction. Origin: induction - g. Therme,... Read More
Parthenogenesis
To reproduce, by definition, means to produce new offspring. The process is referred to as reproduction, which is one of the... Read More
Cell determination
Definition noun The process in which a previously undifferentiated cell is already programmed to become a specific cell type... Read More
The Evolutionary Development of Multicellular Organisms
The beginning of the Cambrian era saw a widespread arrival of multi-cellular organisms, particularly in the form of sponges.... Read More
Anabolic steroid
Definition noun, plural: anabolic steroids Any of the synthetic steroid hormones (androgens) that promote muscle and bone... Read More
Teratogenesis
Definition noun The development of structural or functional malformations in an embryo or a fetus Supplement Abnormalities... Read More
Autoimmune disease
Definition noun, plural: autoimmune diseases A type of disease as a result of an immune response of the body against own... Read More
Sex reversal
Definition noun Change of sexual identity in animals as influenced by an environmental variable, also by surgical or... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
A posteriori
A posteriori 1. (Science: logic) Characterising that kind of reasoning which derives propositions from the observation of... Read More
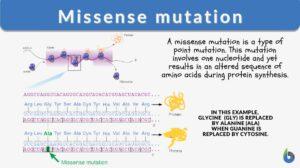
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Autoimmunity
Definition noun, plural: autoimmunities A type of immunity wherein the immune response is directed against own body,... Read More
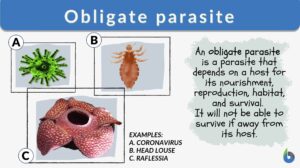
Obligate parasite
Parasitism is a form of symbiosis that occurs between a parasite and its host. The parasite is the organism that generally... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Abscisic acid
Abscisic acid (Science: biochemistry) a lipid hormone that inhibits cell growth in plants, it is associated with fruit drop,... Read More
Eclipse phase
Eclipse phase --> eclipse period The time between infection by (or induction of) a bacteriophage, or other virus, and the... Read More
Eclipse period
Eclipse period The time between infection by (or induction of) a bacteriophage, or other virus, and the appearance of mature... Read More
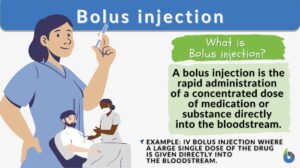
Bolus injection
A bolus injection is the act of administering a dose of medication or substance directly into the bloodstream by injection.... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
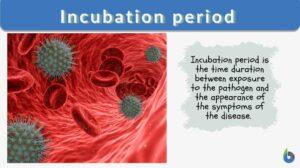
Incubation period
Incubation Period Definition The incubation period is the time duration between exposure to the pathogen and the appearance... Read More
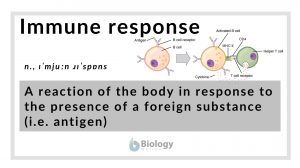
Immune response
Immune Response Definition An immune response is defined as the reaction of the body in response to the presence of a... Read More
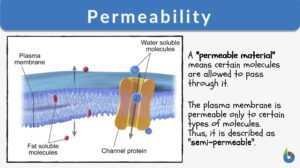
Permeability
Permeability Definition What is permeability? In earth science, its definition is this: "the ability of any material such... Read More