Search Results for: promoter
Promoter gene
Definition noun, plural: promoter genes (genetics) A site in a DNA molecule at which RNA polymerase and transcription... Read More
Down promoter mutation
Down promoter mutation (Science: molecular biology) a mutation (a change in base pair sequence) in a promoter region, this... Read More
Promoter insertion
promoter insertion (Science: molecular biology) activation of a gene by the nearby integration of a virus. The long-terminal... Read More
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Eukaryotic Gene Structure In prokaryotes the DNA is located in the... Read More
Transcription (biology)
In biology, transcription is the process of transcribing or making a copy of the genetic information stored in a DNA strand... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
Pribnow box
Pribnow box --> promoter (Science: molecular biology) A region of dNA to which rNA polymerase binds before initiating the... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Enhancer element
Enhancer element (Science: molecular biology) a dna sequence, present in the genomes of higher eukaryotes and of various... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Transactivation
Definition noun, plural: transactivations (molecular biology, genetics) The stimulation of transcription by expressing an... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Repressor protein
Definition noun, plural: repressor proteins A protein in which its binding to the operator inhibits the transcription of one... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Mature mRNA
Mature mRNA Definition Mature mRNA is the completely processed mRNA molecule in the cell of eukaryotes. The mRNA is a type... Read More
Base pair substitution
Definition noun, plural: base pair substitutions A type of mutation involving replacement or substitution of a single... Read More
Recombinant DNA
Definition noun Genetically-engineered DNA molecule formed by splicing fragments of DNA from a different source or from... Read More
Molecular Basis of Temperature-Dependent Gender of Red-Eared Slider Turtle
Imagine a child inside a womb with a sex yet to be decided not by the pair of sex chromosomes but by the ambient temperature... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Genetic Control – On and Off Genes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. This lesson looks at the various factors involved that affect growth and... Read More
Gene Action – Operon Hypothesis
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Some genes are switched on or off depending on environmental conditions. The... Read More
Precursor mRNA
Definition noun plural: precursor mRNAs An immature or incompletely processed mRNA molecule in eukaryotes that needs to be... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: cyclic adenosine monophosphates (biochemistry) A cyclic form of adenosine monophosphate that... Read More
Up mutation
up mutation (Science: molecular biology) refers to any mutation in the promoter region of a gene which can trigger... Read More
Long-terminal repeats
Long-terminal repeat (Science: molecular biology) identical dna sequences, several hundred nucleotides long, found at either... Read More
Stimulatory protein 1
stimulatory protein 1 An rNA polymerase II transcription factor in vertebrates; binds to dNA in regions rich in G and C... Read More
Control element
Control element generic term for a region of dna, such as a promoter or enhancer adjacent to (or within) a gene that allows... Read More
Expression vector
Definition noun, plural: expression vectors A plasmid containing the required regulatory sequences specifically used for the... Read More
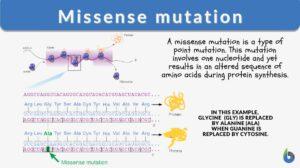
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Point mutation
Definition noun, plural: point mutations (genetics) A small-scale mutation characterized by a change of only one nucleotide... Read More