Search Results for: biochemistry
Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants
Biochemistry & Molecular Biology of Plants ... Read More
Biochemistry
Definition noun The study of the structure and function of cellular components, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids,... Read More
Origins of Life : On Earth and in the Cosmos (2nd Ed)
Origins of Life : On Earth and in the Cosmos ... Read More
Pyruvic acid
What is Pyruvic Acid? Pyruvic acid is an organic acid that occurs as an intermediate in many metabolic processes. It occurs... Read More
First-order kinetics
What is a First-Order Kinetics (First-Order Reaction)? First-order kinetics refers to a reaction wherein the overall rate... Read More
Energy coupling
What is Energy Coupling? Work, whether it be physical or biological, requires energy to be expended. In biological... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Biochemical Genetics
Definition noun A branch of genetics at a biochemical level and in which the relationship of genes and their control over... Read More
Biomolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral, group of atoms that can exist alone in a free state while its characteristic... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Activation
Definition noun (general) The state or the process of being active and/or effective (biochemistry) The process of making a... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Molecular biology
molecular biology (Science: study) The study of the biochemistry of cells, it is closely linked to cell biology, in... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Nucleotide
Nucleotide Definition A nucleotide is regarded as the basic building block of nucleic acid (e.g. DNA and RNA). A nucleic... Read More
Renaturation
Definition noun, plural: renaturations (molecular biology) The conversion of denatured protein or nucleic acid to its native... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Autophosphorylation
Definition noun (biochemistry) The phosphorylation of the kinase through its own enzymatic... Read More
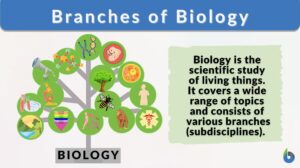
Branches of biology
What is a Branch of Biology? A branch of biology is a specialized field or a sub-discipline in a much broader field of... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More
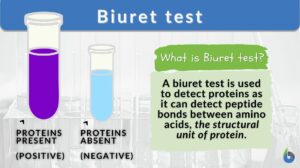
Biuret test
In this article we will answer the following three questions: What is a Biuret Test? What does biuret test for? What is... Read More


![Botany n., [ˈbɑt.ə.ni/] botany definition and example](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/botany-definition-and-example-300x168.jpg)





![Biology n., [baɪˈɑlədʒi] Definition: scientific study of life](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/biology-definition-and-branches-of-biology-300x168.jpg)