Search Results for: down-regulation
Down-regulation
Down-regulation (Science: physiology) development of a refractory or tolerant state consequent upon repeated administration... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Feedback mechanism
Feedback Mechanism Definition What is a feedback mechanism? A feedback mechanism is a physiological regulation system in a... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Density dependent limiting factor
What Is A Density-Dependent Limiting Factor? Density-dependent limiting factors are limiting factors, which, depending on... Read More
Kidneys and Regulation of Water and Inorganic Ions
Renal Functions Kidneys remove/add substances from/to the plasma. Regulate water concentration, inorganic ion... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Principles of Hormonal Control Systems
Hormones are chemical messengers that enter the blood directly upon their secretion from endocrine glands. A single gland or... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
Homeostasis of Organism Water Regulation
Osmoregulation Osmoregulation is the regulation of water concentrations in the bloodstream, effectively controlling the... Read More
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Eukaryotic Gene Structure In prokaryotes the DNA is located in the... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Regulation of Biological Systems
Regulation of Biological Systems tutorials are focused on the modulation of biological systems from cell to population... Read More
Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Integumentary system
Integumentary System Definition The integumentary system is the outermost layer of the body. The animal body, in... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Circulation
Blood Blood is composed of a liquid, plasma, and blood cells such as erythrocytes (red blood cells,) leukocytes (white... Read More
Characteristic
Characteristics Definition We can define characteristics as qualities or features that describe the distinctive nature or... Read More
Cell adhesion
Cell Adhesion Definition Cell adhesion is the process in which a cell uses a specialized complex of proteins to get... Read More
Hypothalamus
Definition noun, plural: hypothalami A small region of the forebrain comprised of several small nuclei, located between the... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Hypotonic solution
Hypotonic Solution Definition What is a hypotonic solution? It refers to a solution that contains a lower amount of solute... Read More
Density dependent factor
Density-dependent factors are the limiting factors of an ecosystem that regulate population growth in a density-dependent... Read More
Regulation of Organic Metabolism, Growth and Energy Balance
Organic Metabolism Events of Absorptive and Post-absorptive States. The absorptive state is the period during which... Read More
Sugar Homeostasis
Blood Sugar Regulation As described in Cell Biology tutorials, the body requires volumes of glucose in order to create ATP.... Read More
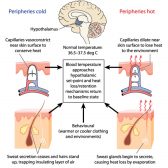
Temperature Regulation in Animals
Control of Temperature in Homeotherms Animals capable of temperature regulation within a given range are deemed homeotherms... Read More
Glucocorticoid
Definition noun, plural: glucocorticoids Any of a group of corticosteroids involved in carbohydrate metabolism (e.g.... Read More
Population
Living organisms typically prefer to live, grow, and survive in groups. Except for some species that prefer solitude - both... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Adipose tissue
Adipose Tissue Definition Adipose tissue, a specialized variety of connective tissue, is composed of lipid-rich cells known... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More