Search Results for: gene synthesis
Gene synthesis
Gene synthesis (Science: molecular biology) The complete synthesis of a gene using a dna synthesiser (gene machine), or the... Read More
Protein synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process of creating protein molecules. In biological systems, it involves amino acid synthesis,... Read More
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
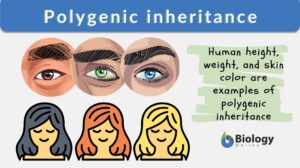
Polygenic inheritance
Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many... Read More
Lipogenesis
Lipogenesis Definition Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat to store biochemical energy for later metabolic... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
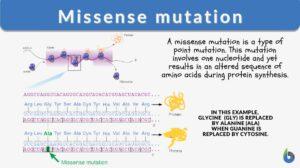
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
Genetic material
Genetic Material Definition What is genetic material? Genetic material is the hereditary substance in the cell. It carries... Read More
Genetic variability
Genetic Variability Definition Genetic variability refers to the tendency of individual genetic characteristics in a... Read More
Mature mRNA
Mature mRNA Definition Mature mRNA is the completely processed mRNA molecule in the cell of eukaryotes. The mRNA is a type... Read More
Messenger ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: messenger ribonucleic acids mes•sen•ger ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈmɛ.sɪn.dʒəɹ... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Maternal-effect gene
Definition noun, plural: maternal-effect genes (1) A gene from the mother's genome in which its phenotype in the zygote is... Read More
Precursor mRNA
Definition noun plural: precursor mRNAs An immature or incompletely processed mRNA molecule in eukaryotes that needs to be... Read More