Search Results for: salts
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Inorganic salt
Definition noun, plural: inorganic salts A salt that lacks C-H bonds Supplement A salt is defined as the neutral ionic... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Inorganic compound
Inorganic Compound Definition An inorganic compound is a chemical compound lacking both carbon-carbon (C-C) and... Read More
Interstitial fluid
Definition noun The fluid found in the intercellular spaces composed of water, amino acids, sugars, fatty acids,... Read More
Bone matrix
Bone Matrix Definition Bone matrix refers to the matrix component of bone tissue. It provides the structural framework and... Read More
Balanced diet
What is a balanced diet? What is the definition of a balanced diet? A nutritionally balanced diet fulfills all nutritional... Read More
Chromaffin cell
Definition noun, plural: chromaffin cells Any of the cells (mostly found) in adrenal medulla and in other ganglia of the... Read More
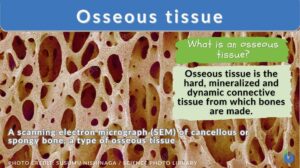
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
Abiotic factor
An abiotic factor is a non-living element of the environment that influences the way organisms and ecosystems function. Some... Read More
Hepatocyte
Definition noun, plural: hepatocytes Any of the large, polygonal-shaped cells in the liver. Supplement Hepatocytes are the... Read More
Facilitated diffusion
Facilitated diffusion is the transport of substances across a biological membrane from an area of higher concentration to an... Read More
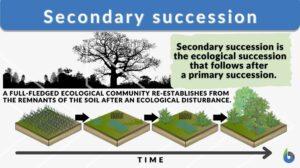
Secondary succession
We all have come across news where forest lands got destroyed by wildfires. Or sometimes we have read about an entire... Read More
Reducing sugar
Reducing Sugar Definition What is reducing sugar? The type of sugar that acts as the reducing agent and can effectively... Read More
Stearic acid
Definition noun, plural: stearic acids A eighteen-carbon fatty acid, with the formula: C18H36O2 Supplement A fatty acid is a... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Phenol coefficient
Chemical disinfectants are categorized based on the power of their disinfection for microbes and viruses. Strong... Read More
Calcification
Calcification (Science: biochemistry) The process by which organic tissue becomes hardened by a deposit of calcium salts... Read More
Rhizophora
Definition noun (botany) A genus of the family Rhizophoraceae which includes the true mangroves Supplement Rhizophora is a... Read More
Amphipathic
Amphipathic Definition Amphipathic is a word used to describe a chemical compound containing both polar (water-soluble) and... Read More
Open circulatory system
Definition noun A type of circulatory system wherein the hemolymph bathes the organs and tissues directly thus there is no... Read More
Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes
Diffusion Diffusion is essentially the movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower... Read More
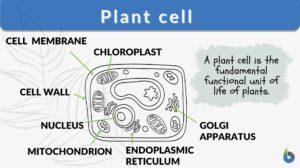
Plant cell
Plant Cell Definition A plant cell refers to any cell of a plant. It is the structural and functional unit of plants. Plant... Read More
Primary producers
'Primary producers (also called simply as producers) are the autotrophs capable of producing organic compounds from light... Read More