Search Results for: series
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Carbohydrate
Carbohydrate Definition A biomolecule refers to any molecule that is produced by living organisms. As such, most of them... Read More
Myeloblast
Definition noun, plural: myeloblasts A precursor cell that gives rise to a promyelocyte during... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Granulocyte
Definition noun, plural: granulocytes A leukocyte characterized by the presence of numerous staining granules in the... Read More
Mononuclear leukocyte
Definition noun, plural: mononuclear leukocytes A leukocyte characterized by having a nucleus with only one lobe, as opposed... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis Definition What is chemiosmosis? In biology, chemiosmosis refers to the process of moving ions (e.g. protons)... Read More
Vertebral column
Definition noun, plural: vertebral columns The series of vertebrae that extend from the cranium to the coccyx, and serves as... Read More
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the tendency not to stray from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. Such conditions must be... Read More
Catabolism
Catabolism Definition Catabolism is the branch of the metabolic process that breaks down complex, big molecules into... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Megakaryoblast
Definition noun, plural: megakaryoblasts A precursor cell that develops into a promegakaryocyte during... Read More
Promegakaryocyte
Definition noun, plural: promegakayocytes A precursor cell in the thrombocytic series that arises from a megakaryoblast and... Read More
Krebs cycle
Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a fundamental metabolic pathway that... Read More
Macrophage
Definition noun, plural: macrophages A leukocyte whose main function is to eliminate cellular debris and foreign particles... Read More
Plant Metabolism
Introduction Plants are responsible for incredible feats of molecular transformation. The processes are always being... Read More
The Psychobiology of Hysteria
Editorial Hysteria is often regarded as the archetypal psychodynamic illness. Freud carried out much of his early work on... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo Minns Submitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009. Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
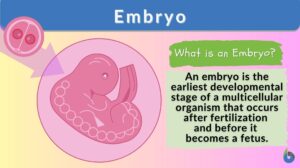
Development
1. The act of developing or disclosing that which is unknown; a gradual unfolding process by which anything is developed, as... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
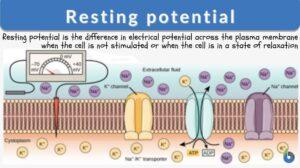
Resting potential
Resting Potential Definition The resting potential of a cell is defined as the difference in electrical potential across... Read More
Homologous
Homologous Definition What is homologous? In general science, the word “homologous” is used to show a degree of... Read More
Lymphocyte
Definition noun, plural: lymphocytes The white blood cell of the blood derived from the stem cells of the lymphoid series of... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More