Search Results for: interphase
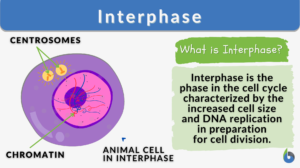
Interphase
Interphase is the critical period in the eukaryotic cell cycle characterized by a sequence of events like the G1 phase where... Read More
Interkinesis
Definition noun Interphase II, i.e. a short resting period occurring between meiosis I and meiosis II Supplement Meiosis is... Read More
Cell cycle
Definition noun (cell biology) The sequence of growth and division of a cell, and consists of a series of biological... Read More
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
Gap 1 phase
Definition noun (cell biology) The first period in the interphase wherein the cell primarily grows in cell... Read More
Gap 2-M DNA damage checkpoint
Definition noun (cell biology) A control mechanism in G2 phase of the cell cycle that ensures the cell is ready for cell... Read More
Gap 2 phase
Definition noun (cell biology) A sub-phase in the interphase of the cell cycle wherein the cell continues to grow and then... Read More
Synthesis phase
Definition noun (cell biology) A sub-phase in the interphase wherein the cell primarily duplicates its DNA via... Read More
Cytokinesis
The cell cycle of eukaryotes is a cyclical series of biological events that certain asexual cells go through. The cell cycle... Read More
Meiosis and Alternation of Generations
Review of Mitosis: Cell Cycle The cell cycle contains the process in which cells are either dividing or in between... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
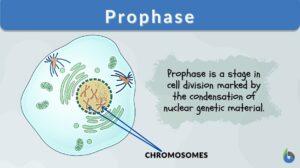
Mitotic phase
Definition noun The phase in the life cycle of a cell highlighted by chromosomal separation resulting into two identical... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Gap 0 phase
Definition noun The phase in the cell cycle wherein the cell is in inactive or non-cycling state following cell... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Nuclear body
Definition noun plural: nuclear bodies nu·cle·ar bod‧y, ˈnjuː.kli.ər ˈbɒdi Any of the prominent non-membraned,... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
Euchromatin
Definition noun A slightly packed or partially condensed form of chromatin that contains structural genes and is usually... Read More
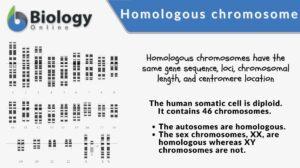
Homologous chromosome
A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Nucleoplasm
Definition noun plural: nucleoplasm nu·cle·o·plasm, ˈnjuːklɪəˌplæzəm (cell biology) The protoplasm of the... Read More
Nuclear matrix
Definition noun plural: nuclear matrices (cell biology) A 3-dimensional filamentous protein network that extends... Read More
Dinoflagellate
A dinoflagellate is a flagellate algae characterized by their two flagella of unequal length. One of the flagella is lying... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Facultative heterochromatin
Definition noun Heterochromatin that may lose its condensed state and becomes genetically active Supplement Heterochromatin... Read More
Polytene chromosome
polytene chromosome (Science: cell biology) giant chromosomes produced by the successive replication of homologous pairs of... Read More
Living things
Living Things Definition A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Heterochromatin
Definition noun Highly condensed, tightly packed form of chromatin, as opposed to the lightly packed... Read More
Constitutive heterochromatin
Definition noun Regions on chromosomes that are condensed permanently, genetically inactive, and always in the same position... Read More