Search Results for: yeast
Active dry yeast
Definition noun A form of dry yeast in which the yeasts are not killed but made dormant through dehydration, and return to... Read More
Cultivated yeast
Definition noun, plural: cultivated yeasts Yeast that is grown in cultures for specific purposes such as bread making,... Read More
Fermentation
Fermentation Definition What is fermentation? Fermentation is the breaking down of sugar molecules into simpler compounds... Read More
Anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic Respiration Definition What is anaerobic respiration? Anaerobic (cellular) respiration is a respiratory process... Read More
Cell theory
What Is Cell Theory? Biological cell theory explains the idea of organismal constitution, structure, and function. It... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
Reproduction
Reproduction Definition Reproduction is a biological phenomenon of producing offspring/s. i.e. more of its kind. Depending... Read More
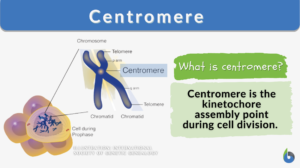
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
saccharomyces cerevisiae (Science: fungus) A species of yeast which is an important model organism for biological study,... Read More
Shuttle vector
Definition noun A vector that can replicate in more than one host organisms or two different cell types (e.g. a prokaryotic... Read More
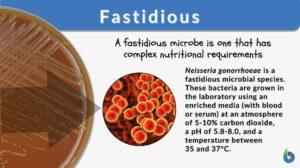
Fastidious
Fastidious Definition We can define fastidious as a term used in microbiology to denote a species that lacks the ability to... Read More
Facultative anaerobe
Facultative Anaerobe Definition What does facultative anaerobe mean? Facultative organisms are the most adaptable... Read More
Protein Activity and Cellular Metabolism
Protein Binding Sites The ability of various molecules and ions to bind to specific sites on the protein surface forms the... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Phenol coefficient
Chemical disinfectants are categorized based on the power of their disinfection for microbes and viruses. Strong... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Pasteur effect
Definition noun The inhibiting effect of oxygen on the fermentation process. Supplement The effect was discovered in 1857 by... Read More
Psychrophile
Definition noun, plural: psychrophiles An organism that thrives in cold temperatures, i.e. ranging from −20 °C to +10... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Electroporation
Definition noun, plural: electroporations A non-chemical method that transfers the genetic material into the recipient cell... Read More
Industrial Microbiology
Definition noun Related to environmental, social and economic importance that are engaged in the utilization of... Read More
Beta-amylase
'Definition noun, plural: beta-amylases A form of amylase found in bacteria, molds, yeasts, and the seeds of plants that... Read More
RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
Definition noun A DNA polymerase enzyme that catalyzes the process of reverse transcription. Supplement This enzyme... Read More