Search Results for: genome
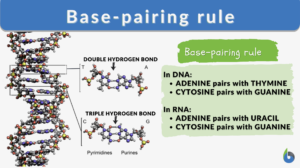
Base-pairing rule
Base-pairing Rules Definition The base-pairing rules are rules that apply during the pairing between one purine and one... Read More
Parthenogenesis
To reproduce, by definition, means to produce new offspring. The process is referred to as reproduction, which is one of the... Read More
Allotetraploid
Allotetraploid Definition An allotetraploid is an organism with four sets of chromosomes (4n). This is in contrast to the... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
Repeated sequences
Definition noun (molecular biology) Multiple copies of nucleotide sequences in the nucleic acids (i.e. DNA or RNA)... Read More
Single-stranded DNA
What is single-stranded DNA? DNA is the material that living organisms possess that carries their genetic make-up. DNA and... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Repetitive DNA
Definition noun (molecular biology) Repetitive nucleotide sequences in the DNA throughout the genome Supplement The... Read More
Retrotransposon
Definition noun, plural: retrotransposons A transposon that is amplified via reverse transcription, i.e. the DNA element is... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Prokaryotic Ancestor of Mitochondria: on the hunt
The alphaproteobacteria have been widely cited as the closest relative-- and possibly the prokaryotic ancestor -- of the... Read More
Genome shuffling
Recombination of whole genomes. One example is protoplasm... Read More
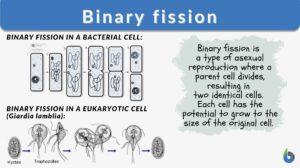
Binary fission
Binary Fission Definition What is binary fission? In biology, binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where a... Read More
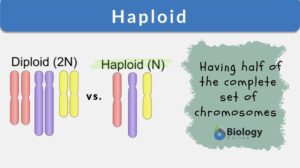
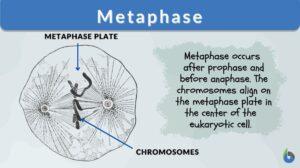
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
Transgenic
Definition adjective Of, pertaining to, or relating to an organism that has genes from another organism put into its genome... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
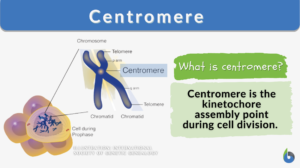
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
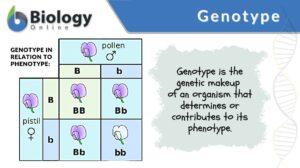
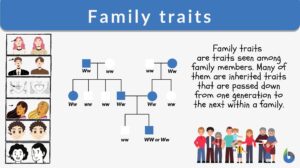
Family traits
When one thinks of family, they often think of persons who are blood-related to each other as parents to their children and... Read More
Zygotic-effect gene
Definition noun, plural: zygotic-effect genes (1) Any of the genes expressed in the early embryo. (2) Any of the genes... Read More
Interspersed repeat
Definition noun, plural: interspersed repeats A type of repeated sequence in which the copies are dispersed throughout the... Read More
Chloroplast DNA
Definition noun plural: chloroplast DNAs DNA in the chloroplast that carries the code for proteins and RNAs essential to... Read More
Genetic material
Genetic Material Definition What is genetic material? Genetic material is the hereditary substance in the cell. It carries... Read More