Search Results for: precursor
Precursor mRNA
Definition noun plural: precursor mRNAs An immature or incompletely processed mRNA molecule in eukaryotes that needs to be... Read More
Mature mRNA
Mature mRNA Definition Mature mRNA is the completely processed mRNA molecule in the cell of eukaryotes. The mRNA is a type... Read More
Myeloblast
Definition noun, plural: myeloblasts A precursor cell that gives rise to a promyelocyte during... Read More
Zymogen granules
Definition noun The granules in the cytoplasm of secretory cells containing the zymogen Supplement Zymogen granules are... Read More
Lipotropin
Definition noun, plural: lipotropins A polypeptide hormone of the anterior pituitary gland, presumably acts by promoting fat... Read More
Differentiation
Differentiation in biology is the process where less specialized cells undergo changes to develop specialized structures and... Read More
Promegakaryocyte
Definition noun, plural: promegakayocytes A precursor cell in the thrombocytic series that arises from a megakaryoblast and... Read More
Chemosynthesis
Definition noun, plural: chemosyntheses The production of a more complex chemical compound by combining two or more simpler... Read More
Megakaryocyte
Definition noun, plural: megakaryocytes A large cell in the bone marrow with characteristic lobulate nucleus and is... Read More
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Eukaryotic Gene Structure In prokaryotes the DNA is located in the... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Histiocyte
Definition noun, plural: histiocytes A reticular connective tissue macrophage or a dendritic cell, derived from the bone... Read More
Omega-6 fatty acid
Definition noun, plural: omega-6 fatty acids A type of polyunsaturated fatty acid in which the first double bond is between... Read More
Angiotensinogen
Definition noun An alpha-2 globulin protein that is found in the bloodstream and release into circulation mainly by the... Read More
Abiogenesis
Definition noun plural: abiogeneses a·bi·o·gen·e·sis, eɪbaɪəʊˈdʒɛnəsɪs (1) The idea that primitive life... Read More
Megakaryoblast
Definition noun, plural: megakaryoblasts A precursor cell that develops into a promegakaryocyte during... Read More
Progenitor
progenitor A precursor, ancestor; one who begets. Origin:... Read More
Pribnow box
Pribnow box --> promoter (Science: molecular biology) A region of dNA to which rNA polymerase binds before initiating the... Read More
Deoxythymidine
Definition noun plural: deoxythymidines A pyrimidine nucleoside that has thymine attached to the pentose sugar... Read More
Parthenogenesis
To reproduce, by definition, means to produce new offspring. The process is referred to as reproduction, which is one of the... Read More
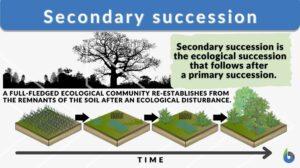
Secondary succession
We all have come across news where forest lands got destroyed by wildfires. Or sometimes we have read about an entire... Read More
Enzyme activation
Enzyme activation conversion of an inactive form of an enzyme to one possessing metabolic activity. It includes 1)... Read More
Erythroblast
Definition noun, plural: erythroblasts A nucleated red blood cell that develops into a reticulocyte Supplement The blood... Read More
De novo pathway
Definition noun, plural: de novo pathways (biochemistry) A biochemical pathway where a complex biomolecule is synthesized... Read More
Thyrotroph
Definition noun, plural: thyrotrophs The cell in the anterior pituitary that particularly releases thyroid-stimulating... Read More