Search Results for: sequence
Signal sequence
Definition noun A sequence of amino acid residues bound at the amino terminus of a nascent protein during protein... Read More
Frameshift mutation
Define Frameshift Mutation What is a frameshift mutation? In biology, insertions or deletions of nucleotides in the coding... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Leader sequence
Definition noun (1) 5' UTR (five prime untranslated region); the section of mRNA and DNA beginning at the +1 position up to... Read More
Conserved sequence
Conserved sequence (Science: molecular biology) a base sequence in a dna molecule (or an amino acid sequence in a protein)... Read More
Dna sequence analysis
Dna sequence analysis (Science: molecular biology) determination of the nucleotide Sequence of a length of dna. Typically,... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
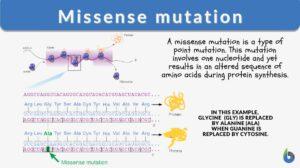
Missense mutation
What is a missense mutation? Literally speaking, a mutation that changes the meaning of the encoded gene sequence is the... Read More
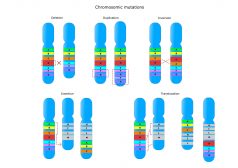
Chromosome Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. By nature, the genetic information from both parents is expected to be seen... Read More
Signature sequence
signature sequence short oligonucleotides of unique sequence found in 16S ribosomal RNA of a particular group of... Read More
Carbohydrate sequence
Carbohydrate sequence The sequence of carbohydrates within polysaccharides, glycoproteins, and... Read More
Amino acid sequence
Amino acid sequence The sequence of amino acids as arrayed in chains, sheets, etc., within the protein molecule. this is... Read More
Sequence homology
sequence homology (Science: molecular biology) Strictly, refers to the situation where nucleic acid or protein sequences are... Read More
Consensus sequence
Consensus sequence Of a series of related dna, rna or protein sequences, the sequence that reflects the most common choice... Read More
Genetic Mutations
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Genetic Mutations Genetic mutations are inherited variations in an... Read More
Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds consisting of chains of monomers of... Read More
Role of Golgi Apparatus & Endoplasmic Reticulum in Protein Synthesis
Continued from the previous tutorial that introduces protein synthesis... mRNA and tRNA mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters... Read More
Shine-dalgarno sequence
shine-dalgarno sequence A short stretch of nucleotides on a prokaryotic mRNA molecule upstream of the translational start... Read More
Unique Sequence
A genetic sequence of DNA that is unique, and therefore does not appear anywhere else in the... Read More
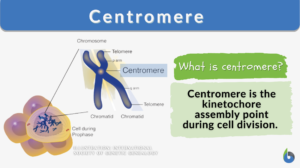
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
Translation
Translation, in general, is the conversion of something into another form, such as a word from one language to another. But... Read More
Pribnow box
Pribnow box --> promoter (Science: molecular biology) A region of dNA to which rNA polymerase binds before initiating the... Read More
Transcription (biology)
In biology, transcription is the process of transcribing or making a copy of the genetic information stored in a DNA strand... Read More
Y chromosome
Y chromosome Definition The Y chromosome constitutes one member of the pair of sex chromosomes within an organism, a common... Read More
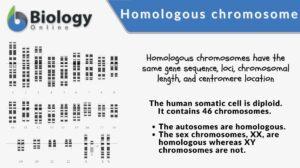
Homologous chromosome
A homologous chromosome pertains to one of a pair of chromosomes with the same gene sequence, loci, chromosomal length, and... Read More
Ribonucleic acid
Ribonucleic Acid Definition noun (uncountable), ribonucleic acids ri·bo·nu·cle·ic ac·id, raɪboʊnjuːkliːɪk... Read More
Nonsense mutation
A nonsense mutation is the type of point mutation that renders the translation process useless by coding for a stop/nonsense... Read More
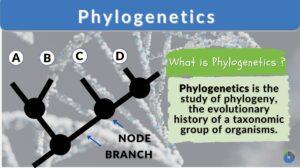
Phylogenetics
Phylogenetics Definition Phylogenetics is the scientific study of phylogeny. It studies evolutionary relationships among... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Polymorphism
Polymorphism Definition The occurrence of two or more different forms or morphs in the population of a species is referred... Read More
Complementary DNA
Definition noun A double stranded DNA produced from the messenger RNA synthesis in a reaction catalyzed by an enzymes... Read More