Search Results for: molecular structure
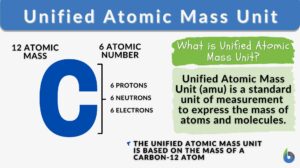
Unified atomic mass unit
Unified Atomic Mass Unit Definition The Unified Atomic Mass Unit (u) (or simply atomic mass unit) refers to the 1/12... Read More
Branches of biology
What is a Branch of Biology? A branch of biology is a specialized field or a sub-discipline in a much broader field of... Read More
Molecular structure
molecular structure The location of the atoms, groups or ions relative to one another in a molecule, as well as the number... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Saccharide
Saccharide Definition What is a saccharide molecule? A saccharide is the unit structure of carbohydrates. In biochemistry,... Read More
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Definition Just like any non-living body possesses a plastic or paper packaging material that keeps the... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Molecular neuroscience
Definition noun A branch of neuroscience that studies the nervous system in terms of its molecular biology, molecular... Read More
Chromosome
Chromosomes Definition Chromosomes are thread-like structures present in the nucleus of plant and animal cells. Chromosomes... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
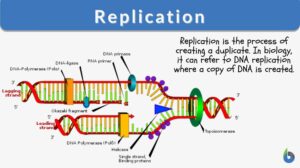
Replication
Replication, in the general sense, is to create a copy or a duplicate. Thus, in biology, replication is commonly associated... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Transfer ribonucleic acid
Definition noun plural: transfer ribonucleic acids trans•fer ri•bo•nu•cle•ic ac•id, ˈtɹænsfɝ... Read More
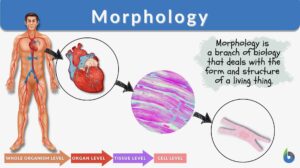
Morphology
Morphology Definition Morphology means the study of the shape and structure of living things from a biological perspective.... Read More





![Biology n., [baɪˈɑlədʒi] Definition: scientific study of life](https://www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/biology-definition-and-branches-of-biology-300x168.jpg)