Homeostasis of Organism Water Regulation
Homeostasis by water regulation
Table of Contents
Osmoregulation
Osmoregulation is the regulation of water concentrations in the bloodstream, effectively controlling the amount of water available for cells to absorb.
The homeostatic control of water is as follows
- A change in water concentration leads to active via negative feedback control
- Osmoreceptors that are capable of detecting water concentration are situated on the hypothalamus next to the circulatory system
- The hypothalamus sends chemical messages to the pituitary gland next to it.
- The pituitary gland secretes anti-diuretic hormone (ADH), which targets the kidney responsible for maintaining water levels.
- When the hormone reaches its target tissue, it alters the tubules of the kidney to become more / less permeable to water
- If more water is required in the bloodstream, high concentrations of ADH make the tubules more permeable.
- If less water is required in the bloodstream, low concentrations of ADH make the tubules less permeable.
This is illustrated by the flow chart below
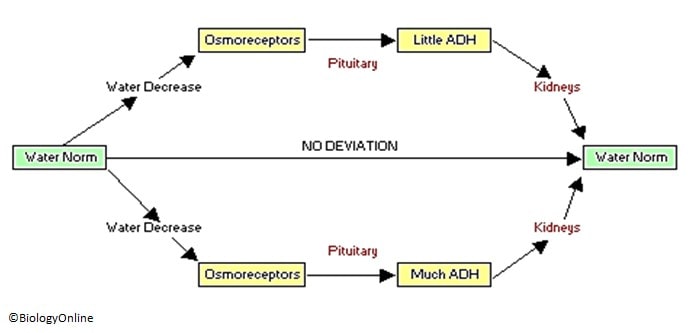
Negative Feedback Control of Water in Animals
Evolutionary Adaptations in Water Regulation
Some of the Adaptation tutorials investigate certain evolutionary adaptations that organisms have achieved through natural selection. This looks at ways in which both animals and plants can be better adapted to cope with extreme environments (desert or wetlands). These changes can be behavioral, physical or anatomical, and in some way promote water regulation. Both plants and animals appear to have adapted to their environment.
More Homeostasis
The body also contains negative feedback control mechanisms for the control of blood sugar concentration and temperature regulation. These types of homeostasis are described on the next tutorials, Sugar Homeostasis and Temperature Regulation in Animals, respectively.
You will also like...

New Zealand’s Unique Geographical History
Explore why New Zealand has such unique flora and fauna, and learn why long periods of geographical isolation. This less..

Respiration
The human respiratory system is an efficient system of inspiring and expiring respiratory gases. This tutorial provides ..

Control of Body Movement
Some of the body movements can be controlled at will, others cannot. The body has a motor program, which is the pattern ..

Homeostatic Mechanisms and Cellular Communication
Homeostasis is the relatively stable conditions of the internal environment that result from compensatory regulatory res..

Geological Periods
Geological periods is a study guide that cites the different geological periods on Earth's timeline. Each has a brief ov..

Still Freshwater & Plants
Plants in lentic habitats have features not found in terrestrial plants. They acquired these features as they adapt to t..
